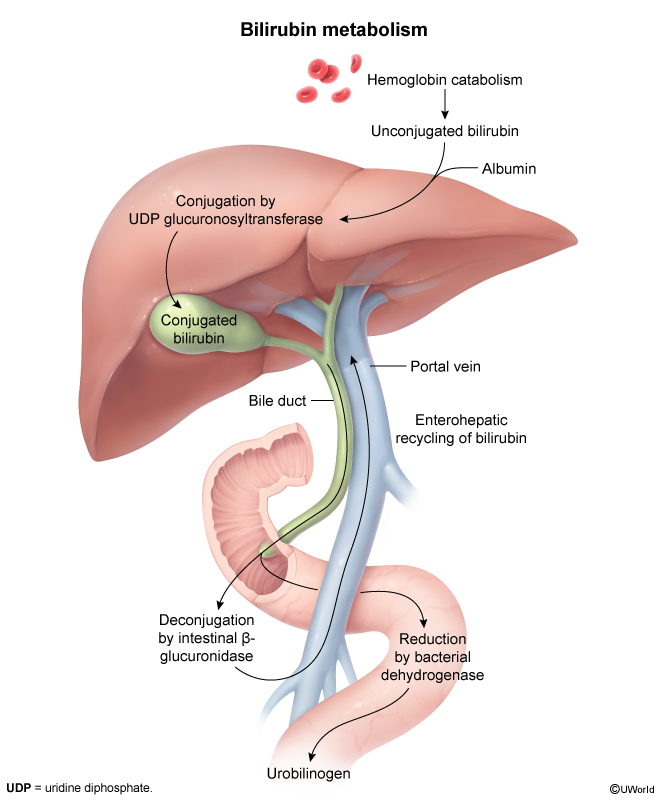
<aside> ⚠️
Pathologic jaundice of the newborn is jaundice which either during the first day of life, has total bilirubin >12, direct bilirubin >2, or shows rate or rise of >5/day.
</aside>
| Type of Jaundice | Onset & Duration | Type of Bilirubin | Key Features | Board Clues / Buzzwords |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physiologic Jaundice | Appears after 24 h | |||
| Peaks 3–5 days (term) | ||||
| Resolves by \~1 week | Unconjugated | No symptoms, well baby, resolves spontaneously | Term baby, jaundice >24h, no other findings | |
| Pathologic Jaundice | Appears <24 h OR very high OR prolonged (>1 wk) | Usually unconjugated | May be due to hemolysis, sepsis, G6PD, ABO/Rh | Early onset (<24 h), fast rise >5 mg/dL/day, lasts >2 weeks |
| Breastfeeding Jaundice | ||||
| ”not breastfeeding enough” | Early onset (1st week) | Unconjugated | Due to poor intake, dehydration | Weight loss, ↓ output, improves with better feeding |
| Breast Milk Jaundice | ||||
| ”enzyme in the milk” | Peaks at 7–10 days | |||
| May persist weeks | Unconjugated | Due to substances in milk inhibiting conjugation | Otherwise well, persists longer but benign | |
| Hemolytic Jaundice (ABO, Rh) | <24 h onset, rapid rise | Unconjugated | Anemia, retics ↑, positive Coombs test | Early jaundice + anemia + hepatosplenomegaly |
| G6PD Deficiency | <24–48 h onset, acute | Unconjugated | Anemia, ↑ retics, Coombs negative, FHx | Male, Mediterranean/Asian, triggers (e.g., fava beans) |
| Infection (Sepsis) | Variable (early/late) | Unconjugated or mixed | Sick baby: fever, poor feeding | Fever + jaundice + poor feeding → always suspect sepsis |
| Crigler-Najjar Syndrome | Early onset, persistent | Severe unconjugated | Genetic UGT deficiency (Type I = severe, Type II = milder) | Very high bili, normal LFTs, no hemolysis |
| Biliary Atresia | Appears after 2 weeks | Conjugated (direct) | Pale stools, dark urine, hepatomegaly | Conjugated jaundice + clay stools + firm liver |
| Neonatal Hepatitis | After 1–2 weeks | Conjugated | Hepatomegaly, poor growth, dark urine | Viral infections common (CMV, hepatitis viruses) |


Inherited Hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert, Crigler-Najjar, Rotor, Dubin-Johnson Syndromes)



